
How to Build an Enterprise Big Data Strategy in 4 Steps
Smart organizations use vast quantities of data to better understand their customers, track inventory, improve logistics and operational processes and make informed business decisions. Successful organizations also understand the importance of managing the burgeoning amounts of data they are creating, and of finding reliable ways to extract value from all that information. Having a big data strategy to effectively and efficiently store, manage, process and apply all that data is critical.
A well-defined and comprehensive big data strategy lays out the steps needed to become a more data-driven — and thus successful — organization. It should incorporate guidelines to help accomplish the data-driven vision and direct the organization to specific business goals. This is easier said than done.
The importance of a big data strategy in the enterprise
Too often enterprise data is stored in silos, in data warehouses or stuck in disparate departmental systems that lack data integration, making it nearly impossible for companies to get a comprehensive view of all their data. Additionally, data quality and variety can vary, the trustworthiness of data sources can vary, and storage and associated costs of data can be high
As a result, building a big data strategy is put on the back burner as enterprises scramble to manage and deal with day-to-day business operations. Without a big data strategy in place, however, enterprises will be dealing with various data-related activities happening simultaneously throughout the organization. This can create duplicate efforts, or worse, competing efforts that are not in alignment or that do not clearly meet the company’s long-term strategic objectives.
A well-defined big data strategy provides a clear roadmap for the ways in which data will be used to support and improve how business is done. It must be actionable, widely adopted and predicated on an enterprise-wide appreciation that data is an asset that sets up the business for continued success.
Here is a multistep approach to formulating a big data strategy.
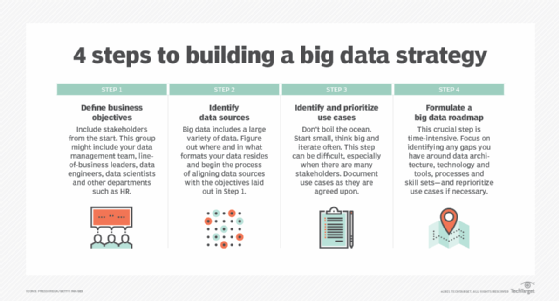
Step 1: Define business objectives
It should come as no surprise that in order to have a successful big data strategy, you must first define what business objectives you are trying to accomplish. Not every business is the same, so there is no one-size-fits-all answer here. However, you should make sure that your strategy aligns to your overall corporate business objectives while also addressing key business problems and key performance indicators. Make sure that stakeholders — including folks from your data management team, line-of-business leaders, data engineers, data scientists and anyone else who will be utilizing your big data stores — are involved right from the start and provide key input on a continuous basis.
Step 2: Identify data sources, processes
The next step involves identifying the variety of your data as well as assessing current business processes, data sources, data assets, technology assets, capabilities and policies at the organization.
Data comes in different formats, including structured, unstructured or semi-structured. It’s not uncommon for an organization to have many varieties of data, including spreadsheets, documents, databases, log files, videos, images and text, among other types.
Once you have identified sources of data, run an assessment on your data strategy. Make sure to address the business objectives you outlined in step one and work from there. For example, if a business objective of your data strategy is to improve customer experience, then your current state assessment would cover any business processes, business models or data assets, including data architecture, that touch customers. When assessing your current state, it’s good practice to interview and involve all relevant employees and stakeholders.
Step 3: Identify and prioritize use cases
Don’t boil the ocean applies here. In formulating a big data strategy, start small, think big, iterate often — and think in terms of use cases. Identify big data use cases that meet your business objectives outlined in step one. Use big data analytics to examine your large volumes of data to uncover hidden patterns, correlations and other insights. These exercises should help you build out and refine use cases.
The next step is to start prioritizing these use cases based on factors such as their business impact, budget needed and resources required. Depending on how many different departments you have represented in the process, narrowing down use cases and prioritizing which ones to start with may be difficult. Remember to stay focused, write down use cases as they are agreed upon and work as a group to come up with a plan.
Step 4: Formulate a big data roadmap
Once you have identified your business objectives, gotten an understanding of your data and current capability state and identified use cases, you can now begin to formulate a big data roadmap.
This crucial step is often the most time-intensive step for organizations. When creating your big data roadmap, remember that the roadmap is just an outline. You can continue to iterate and evolve your roadmap over time. With that in mind, picture your desired end state and work backward, making sure the end goal is precise, certain and direct.
The roadmap exercise should focus on identifying any gaps you have around data architecture, technology and tools, processes and skill sets. The gap analysis will likely prompt a review of the use cases prioritized in step three. Again, stakeholders will play a key role in prioritizing these initiatives based on complexity, budget and cost/benefits.
How to ensure your big data strategy is adopted
No strategy is effective without a plan to for ensuring it is actually used throughout your entire organization. Therefore, it’s important to consider the following:
- Identify infrastructure challenges. To effectively leverage your data, especially data living in historical databases or antiquated systems, you may need to make infrastructure changes which may not be compatible with big data technology. Identify areas where infrastructure changes will be necessary and involve your stakeholders to ensure different departments and users don’t lose access to critical data.
- Evaluate employee resources. It’s one thing to create a killer strategy, but without the right roles and skill sets in place, the strategy will go nowhere. Don’t underestimate your human resources department in your big data strategy. Your big data team must have the necessary skill sets needed to make sense of data, and then translate those findings to various line-of-business leaders. Without a good team, the entire vision may suffer. HR can play a critical role in finding and hiring the talent you need. Also, don’t underestimate the capabilities of current employees. Sometimes with a little reskilling or upskilling your current employees are able to fill critical roles needed to execute your strategy.
- Be agile. You want to make sure that you build flexibility into your roadmap. You need to be able to quickly and easily adjust your budget, employees, use cases and priorities based on the changing circumstances and insights gathered.
Taking the next step in your enterprise big data plan
Staying agile might be the most important principle to live by when implementing a big data strategy. Because data sources and big data technologies are not static, a big data strategy cannot be a one-and-done exercise. But an ongoing, dedicated effort to think strategically about data will pay dividends. A well-thought-out, well-executed and flexible plan will help your enterprise gain valuable business intelligence, make better business decisions and potentially reshape your business strategy.