
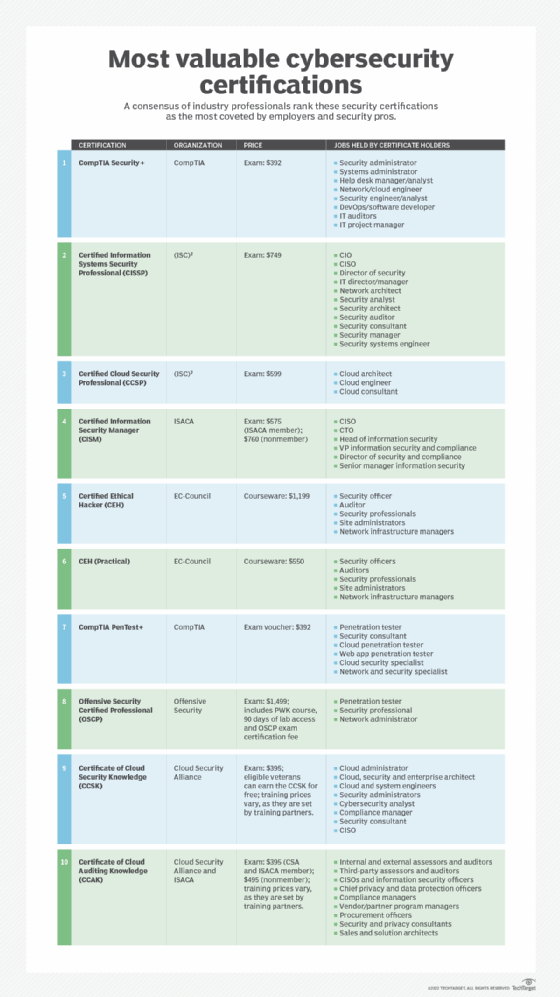
Top 10 Best Cybersecurity Certifications for 2021
Heading into 2021, cybersecurity remains one of the enterprise’s highest priorities as companies continue to support remote working conditions imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. And demand for cybersecurity experts shows no signs of slowing. The Bureau of Labor Statistics has projected that employment of information security analysts will grow 31% from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations.
For those looking to advance their cybersecurity careers or break into the field, cybersecurity certifications can help in landing jobs, boosting careers or ensuring against a job loss — provided you choose wisely. Our guide provides insight into the 10 cybersecurity certifications deemed most valuable for aspiring and seasoned cybersecurity professionals:
- CompTIA Security+;
- (ISC)2 Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP);
- (ISC)2 HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP);
- ISACA Certified Information Security Manager (CISM);
- EC-Council Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH);
- EC-Council CEH (Practical);
- CompTIA PenTest+;
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP);
- Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK); and
- vendor-specific security certifications.
In building this list of top 10 cybersecurity certifications, we talked to a broad range of people in the security industry. We heard from course providers and consultants, such as Cybrary and CyberVista; talked to a professor from University of Maryland Global Campus; sought advice from security providers, such as Cisco and Fortinet; and contacted the leading trade groups and certification providers, such as CSA, CompTIA, EC-Council, ISACA, (ISC)2, Global Knowledge and Offensive Security.
The list starts off with basic, entry-level and management track certifications and then moves on to the offensive security certifications for hands-on penetration testers (pen testers) and certified ethical hackers. It concludes with a mini 10 list of top vendor-specific certifications. Security professionals typically need a mix of all three types of certifications: management training, hands-on and vendor-/product-specific knowledge.
CompTIA Security+
Most security pros say that IT support technicians and admins — or people looking to get into the security field — should start with the CompTIA Security+ certification.
Upon completing the Security+ certification, students will have the skills and knowledge required to install and configure systems used to secure networks, applications and mobile devices. They will also be prepared to take part in risk mitigation activities, perform and respond to threat analysis, and work with knowledge of all applicable laws, policies and regulations. The exam consists of 90 multiple-choice and performance-based questions. Students have 90 minutes to complete the exam. The exam focuses heavily on performance-based questions. The performance-based emphasis ensures that trainees can troubleshoot quickly and accurately. Passing the exam requires a score of at least 750 out of 900.
Prices
- Exam voucher: $349
- Basic Bundle: $499 (includes exam voucher, one test retake and The Official CompTIA Security+ Study Guide e-book)
- Exam Prep Bundle: $649 (includes exam voucher, one test retake, The Official CompTIA Security+ Study Guide e-book and a 12-month individual license for CertMaster Practice for Security+, a knowledge assessment and certification training companion tool)
- eLearning Bundle: $999 (includes exam voucher, one test retake, a 12-month individual license for CertMaster Learn for Security+, which is a collection of interactive and self-paced instructional lessons with assessments, and a 12-month individual license for CertMaster Labs for Security+)
Jobs held by CompTIA Security+ holders
- security administrator
- systems administrator
- help desk manager/analyst
- network/cloud engineer
- security engineer/analyst
- DevOps/software developer
- IT auditor
- IT project manager
(ISC)2 Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certificate is aimed at people with some hands-on experience in the field and is considered mandatory for career advancement. There are few CISOs or upper-level security executives who have not completed it. First offered in 1994, CISSP is administered by (ISC)². To qualify for CISSP, candidates must pass the exam and have at least five years of cumulative, paid work experience in two or more of the eight domains of the (ISC)² CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK).
The eight domains in the CBK include the following: security and risk management; asset security; security architecture and engineering; communication and network security; identity and access management; security assessment and testing; security operations; and software development security. The exam evaluates expertise across these eight security domains. Passing the exam proves the student has the advanced knowledge and technical skills to effectively design, implement and manage a best-in-class cybersecurity program. The English CISSP Computerized Adaptive Testing exam runs three hours and consists of 150 questions. Students need a score of 700 out of 1,000 to pass the exam. The certification remains valid for three years. The average salary for CISSPs is $131,030.
Prices
- Exam: $699
- Online, instructor-led course: $2,495
Jobs held by CISSPs
- CIO
- CISO
- director of security
- IT director/manager
- network architect
- security analyst
- security architect
- security auditor
- security consultant
- security manager
- security systems engineer
(ISC)2 HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP)
Candidates for the HCISPP must pass the exam and have at least two years of cumulative, paid work experience in one or more knowledge areas of the (ISC)2 HCISPP CBK. The seven domains for the healthcare certification are as follows: healthcare industry; information governance in healthcare; information technologies in healthcare; regulatory and standards environment; privacy and security in healthcare; risk management and risk assessment; and third-party risk management.
Students may substitute legal experience for information governance, and they can substitute information management experience for privacy. Of the two years of experience, students must have spent at least one of those years in the healthcare industry. The exam consists of 125 questions and takes three hours. Students must score a 700 out of 1,000 to pass.
Prices
- Exam: $599
- Online, instructor-led course: $1,645
Jobs held by HCISPPs
- compliance auditor
- compliance officer
- health information manager
- information security manager
- information technology manager
- medical records supervisor
- practice manager
- privacy and security consultant
- privacy officer
- risk analyst
ISACA Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
Launched in 2002 by ISACA, CISM attracts professionals with technical expertise and experience in infosec/IT security and control who want to make the move from team member to management. CISM promises to add credibility and confidence to the candidate’s interactions with internal and external stakeholders, peers, and regulators by dramatically improving security knowledge and skills.
The CISM exam tests IT professionals and validates their expertise and experience in the following domains: information security governance; information risk management; information security program development and management; and information security incident management.
CISM focuses on people who are already working in some capacity in IT or infosec and want to gain more knowledge so they can advance their careers. Eligibility for the test requires five or more years of experience in infosec management; experience waivers are available for a maximum of two years only. The exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions that cover the exam content outline created from the most recent content analysis. Students have up to four hours to complete the exam. CISM certification holders can earn an average salary of $148,622.
Prices
- Exam
- ISACA member price: $575
- Nonmember price: $760
- CISM Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database (12-month online subscription)
- Member: $299
- Nonmember: $399
- CISM Online Review Course (self-paced)
- Member: $795
- Nonmember: $895
- CISM Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, 9th Edition — available in multiple languages
- Member: $120
- Nonmember: $156
- CISM Review Manual, 15th Edition — available in print and e-book
- Member: $105
- Nonmember: $135
Jobs held by CISMs
- CISO
- CTO
- head of information security
- VP, information security and compliance
- director of security and compliance
- senior manager, information security
EC-Council Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
A Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) understands and knows how to look for weaknesses and vulnerabilities in target systems and uses the same knowledge and tools as a malicious hacker but in a lawful and legitimate manner to assess a target’s security posture. The CEH credential, offered by EC-Council, certifies people in the specific network security discipline of ethical hacking from a vendor-neutral perspective.
The CEH credential was developed for the following reasons: establish and govern minimum credentials standards for professional information security specialists in ethical hacking; inform the public that these credentialed individuals meet or exceed the minimum standards; and reinforce ethical hacking as a unique and self-regulating profession. Applicants must have two years of provable work experience in the security field to qualify. The exam runs four hours and consists of 125 questions.
Prices
Jobs held by CEHs
- security officer
- auditor
- security professional
- site administrator
- network infrastructure manager
EC-Council CEH (Practical)
CEH (Practical) consists of a six-hour exam that requires students to demonstrate the application of ethical hacking techniques to solve a security audit challenge. Skills tested include threat vector identification, network scanning, OS detection, vulnerability analysis, system hacking and web app hacking. Students typically take this exam after they have attained the CEH certificate.
Students are given limited time, just like in the real world. The exam was developed by a panel of experienced subject matter experts and includes 20 real-life scenarios with questions designed to validate essential skills required in the ethical hacking domains as outlined in the CEH program. It’s not a simulated exam, but rather, it mimics a real corporate network through the use of live VMs, networks and applications, designed to test skills. Students are presented with scenarios and asked to demonstrate the application of the knowledge acquired in the CEH course to find solutions to real-life challenges. Student pass with a score of 70% and above.
CEH (Practical) certificate holders have mastered the following skills:
- understand attack vectors;
- perform network scanning to identify live and vulnerable machines in a network;
- perform OS banner-grabbing, service and user enumeration;
- perform system hacking, steganography and steganalysis attacks, as well as cover tracks;
- identify and use viruses, computer worms and malware to exploit systems;
- perform packet sniffing;
- conduct a variety of web server and web application attacks, including directory traversal, parameter tampering and cross-site scripting attacks;
- perform SQL injection attacks;
- perform different types of cryptography attacks; and
- perform vulnerability analysis to identify security loopholes in the target organization’s network, communication infrastructure, end systems, etc.
Price
- Exam: $550
- Includes a single CEH (Practical) Aspen Dashboard code that gives students access to the following:
- Upon activation, the Aspen Dashboard access lasts for 365 days, which means students can schedule an exam anytime within this time.
- The dashboard code is valid for one year from date of receipt, which means students have to activate the code within one year or it expires.
- Accommodation of remote proctoring services (booking of slots need to be three days prior the exam date).
- CEH cyber range challenge exam (six hours).
Jobs held by CEH (Practical) holders
- security officer
- auditor
- security professional
- site administrator
- network infrastructure manager

CompTIA PenTest+
Students who have completed CompTIA Security+ and have three to four years of practical experience are good candidates for CompTIA PenTest+. This test assesses the most up-to-date pen testing and vulnerability assessment and management skills required to determine the resiliency of the network against cyber attacks. The test verifies that students have the following skills: plan and scope an assessment; understand legal and compliance requirements; perform vulnerability scanning and pen testing; analyze data; and effectively report and communicate results. The test has a maximum of 85 questions and takes 165 minutes. The passing score is 750 on a scale of 100-900.
Prices
- Exam voucher: $359
- Basic Bundle: $549 (includes exam voucher, one test retake and The Official CompTIA PenTest+ Study Guide e-book)
- Exam Prep Bundle: $699 (includes exam voucher, one test retake, The Official CompTIA PenTest+ Study Guide e-book and a 12-month individual license for CertMaster Practice for PenTest+, a knowledge assessment and certification training companion tool)
- eLearning Bundle: $949 (includes exam voucher, one test retake and a 12-month individual license for CertMaster Learn for PenTest+)
Jobs held by CompTIA PenTest+ holders
- penetration tester
- vulnerability tester
- security analyst level 2
- vulnerability assessment analyst
- network security operations
- application security vulnerability
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
The OSCP certification has become one of the more coveted certificates for hands-on, offensive-minded security professionals. Students must prepare by going through the prep courses and practicing skills in the labs. The OSCP exam has a 24-hour time limit and consists of a hands-on pen test in Offensive Security’s isolated VPN network. Candidates will receive the exam and connectivity instructions for an isolated network for which they have no prior knowledge or exposure. Points are awarded for each compromised host, based on its difficulty and level of access obtained.
Certified OSCPs can identify existing vulnerabilities and execute organized attacks in a controlled and focused manner. They can use or modify existing exploit code to their advantage, perform network pivoting and data exfiltration, and compromise systems that are poorly configured. Completing the 24-hour exam demonstrates persistence and determination. OSCPs have also shown they can think outside the box while managing both time and resources.
Prices
- Penetration Testing with Kali Linux (PWK)
- PWK course + 30 days lab access + OSCP exam certification fee: $999
- PWK course + 60 days lab access + OSCP exam certification fee: $1,199
- PWK course + 90 days lab access + OSCP exam certification fee: $1,349
- Retakes
- OSCP certification exam retake fee: $150
Jobs held by OSCPs
- penetration tester
- security professional
- network administrator
CSA Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
Released in 2011 by CSA, the CCSK course is roughly a 60-40 split between tactical (technical) and strategic (business-driven) subject matter around cloud security. Students must complete this open-book, online exam in 90 minutes. The test consists of 60 multiple-choice questions selected randomly from the CCSK question pool, and students must score at least an 80% to pass. The subject matter covers 16 domains related to cloud security and cloud security governance and regulations.
In completing CCSK, students will gain the following benefits:
- proven competency in key cloud security issues through an organization that specializes in cloud research;
- increased employment opportunities by filling the skills gap for cloud-certified professionals;
- demonstrated technical knowledge, skills and abilities to effectively use controls tailored to the cloud; and
- ability to establish a baseline of security best practices when dealing with a broad array of responsibilities, from cloud governance to configuring technical security controls.
The CCSK exam body of knowledge includes the CSA Security Guidance v4.0, CSA Cloud Controls Matrix and EU Agency for Cybersecurity Cloud Computing Risk Assessment reports.
Price
- Exam: $395
- Training prices vary as they are set by training partners.
Jobs held by CCSKs
- cloud administrator
- cloud, security and enterprise architect
- cloud and system engineer
- security administrator
Vendor-specific security certifications
While there are so many vendor security training programs to comb through, it all basically boils down to the products your company uses, the expertise the staff has available and whether it makes sense to spend the time and money on the training.
Here’s a list of some of the leading vendor security certifications with links to course details, pricing and information on the broad range of certifications many of these vendors offer: