
What is digital identity? | Definition from TechTarget
What is a digital identity?
A digital identity is the collection of data about an individual, organization or electronic device that exists online.
Components of a digital identity
The components of a digital identity include unique identifiers and usage patterns that can be used to recognize individuals or their devices across the digital ecosystem.
Identifiers and authentication
Digital identities are often tied to digital identifiers, such as usernames, passwords or device IDs like Internet Protocol addresses. These identifiers are key components in digital authentication processes, determining how individuals or devices are recognized and verified across the internet.
Data points and attributes
Digital identities encompass a wide array of data points that might include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Username and password combinations.
- Purchasing behaviors or transaction histories.
- Birth dates.
- Social security numbers.
- Online search activities and electronic transactions.
- Medical history.
These elements contribute to the formation of a digital identity by providing a detailed profile of an individual’s or entity’s online interactions and behaviors.
Additionally, digital identities are extensively used by website owners and advertisers to track users and tailor content delivery accordingly. By analyzing a user’s digital footprint, companies can serve targeted advertisements and content that align with the user’s preferences and behaviors.
Privacy and security implications
However, because a profile often includes aspects of a person’s actual identity, digital identities come with privacy and security risks, including identity theft. Pseudonymous profiles can also yield an individual’s identity through cross-site data analysis. While passports and licenses identify users in real life, the inclusion of such personally identifying information (PII) online might pose more risks than benefits for the user.

To mitigate these risks, robust authentication and authorization systems are essential. However, as of now, no universally standardized and verified system comprehensively secures digital identities against all forms of cyberthreats.
The future of digital identities
The ongoing development of technologies and frameworks aims to standardize the way digital identities are managed and protected. This includes efforts to create more secure systems using technologies such as biometric authentication and multifactor authentication for identity verification and authentication that respect user privacy while providing convenience and security.
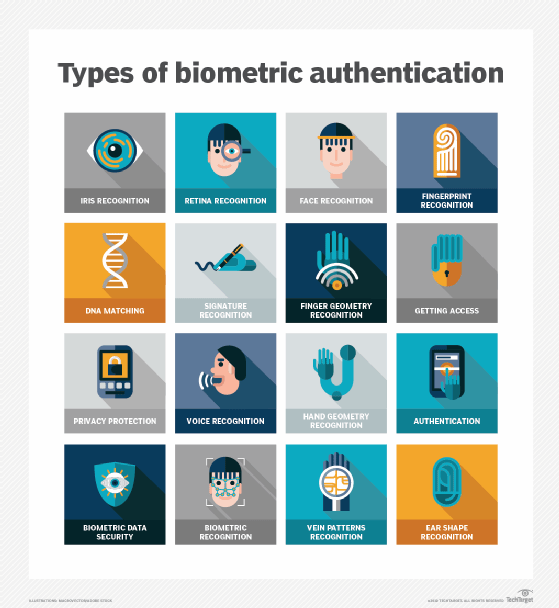
After all, digital identities are an integral part of the online landscape, influencing everything from personalized user experiences to privacy risks. However, as the digital world continues to evolve, so will the mechanisms for managing and protecting these identities, necessitating ongoing vigilance and innovation in digital identity management.
Enterprise identity and access management strategies must include processes for managing and securing three types of digital identity. Learn how to ensure security for three types of digital identity.